Octave Tutorials by Andrew Ng
Updated at: March 11, 2017
part1: basic
numeric
- five add six,
5+6 - three minus two,
3-2 - five multiplied by eight/five times eight,
5*8 - one divided by two/two into one goes,
1/2 - x to the yth power,
x^y
logic
1 == 2 % false, % is comment1 ~= 0 % not equal to1 && 0 % AND1 || 0 % ORxor(1,0) % 异或
PS1(cmd promot): PS1('>> ');
>> a=3
a = 3
>> a=3; %semicolon suppress output
>> b='hi';
>> c=(3>=1);
>> c
c = 1
>> a=pi;
>> a
a = 3.1416
>> disp(a)
3.1416
>> disp(sprintf('2 decimals: %0.2f',a))
2 decimals: 3.14
>> format long
>> a
a = 3.14159265358979
>> format short
>> a
a = 3.1416
matrix & vector
>> A=[1 2;3 4;5 6]
A =
1 2
3 4
5 6
>> A=[1 2;
3 4;
5 6]
A =
1 2
3 4
5 6
>> v=[1 2 3]
v =
1 2 3
>> v=[1;2;3]
v =
1
2
3
>> v=1:0.1:2 % start:increment:end
v =
1.0000 1.1000 1.2000 1.3000 1.4000 1.5000 1.6000 1.7000 1.8000 1.9000 2.0000
>> v=1:6
v =
1 2 3 4 5 6
>> ones(2,3)
ans =
1 1 1
1 1 1
>> C=2\*ones(2,3)
C =
2 2 2
2 2 2
>> w = zeros(1,3) % one by three matrix
w =
0 0 0
>> w=rand(1,3)
w =
0.37811 0.72512 0.89963
>> rand(3,3) % uniform distribution
ans =
0.850304 0.011820 0.684585
0.109987 0.530488 0.862454
0.155507 0.301278 0.619777
>> randn(3,3) % gauls distribution 正态分布
>> eye(4)
ans =
Diagonal Matrix
1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1
>> help eye
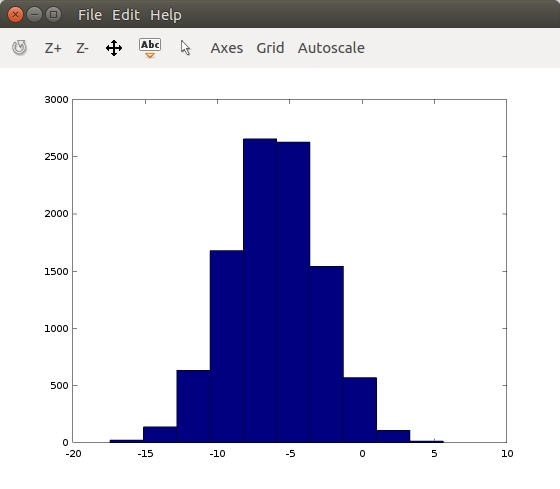
figure
>> w=-6+sqrt(10)\*(randn(1,10000));
>> hist(w)
part2: move data around
>> A=[1 2;3 4;5 6;]
A =
1 2
3 4
5 6
>> size(A)
ans =
3 2
>> size(A,1) % row count
ans = 3
>> size(A,2) % column count
ans = 2
>> v=[1 2 3 4]
v =
1 2 3 4
>> length(v)
ans = 4
>> length(A)
ans = 3
>> pwd
ans = /home/xxx
>> cd octave/
>> ls
featuresX.dat featuresY.dat
>> load featuresX.dat
>> who
Variables in the current scope:
A ans featuresX v
>> featuresX
featuresX =
1234 1
4567 2
1234 3
4567 4
>> whos
Variables in the current scope:
Attr Name Size Bytes Class
==== ==== ==== ===== =====
A 3x2 48 double
ans 1x11 11 char
featuresX 4x2 64 double
v 1x4 32 double
Total is 29 elements using 155 bytes
>> load featuresY.dat
>> clear featuresX
>> whos
Variables in the current scope:
Attr Name Size Bytes Class
==== ==== ==== ===== =====
A 3x2 48 double
ans 1x11 11 char
featuresY 4x1 32 double
v 1x4 32 double
Total is 25 elements using 123 bytes
>> v=featuresY(1:2)
v =
1234
4567
>> save hello.mat v;
>> clear
>> load hello.mat
>> who
Variables in the current scope:
v
>> save hello.txt v -ascii % save as text(ASCII)
>> A=[1 2;3 4;5 6]
A =
1 2
3 4
5 6
>> A(3,2)
ans = 6
>> A(3,:) % ":" means every element along that row/col
ans =
5 6
>> A(:,2)
ans =
2
4
6
>> A([1 3],:)
ans =
1 2
5 6
>> A(:,2)=[10;11;12]
A =
1 10
3 11
5 12
>> A=[A,[100;101;102]] % append another column vector to right
A =
1 10 100
3 11 101
5 12 102
>> B=[1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9]
B =
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
>> C=[A B]
C =
1 10 100 1 2 3
3 11 101 4 5 6
5 12 102 7 8 9
>> C=[A;B]
C =
1 10 100
3 11 101
5 12 102
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
part3: compute on data
>> A=[1 2;3 4;5 6]
A =
1 2
3 4
5 6
>> B=[11 12;13 14;15 16]
B =
11 12
13 14
15 16
>> C=[1 1;2 2]
C =
1 1
2 2
>> A*C
ans =
5 5
11 11
17 17
>> A.*B
ans =
11 24
39 56
75 96
>> A.^2
ans =
1 4
9 16
25 36
>> v=[1;2;3]
v =
1
2
3
>> 1./v
ans =
1.00000
0.50000
0.33333
>> log(v)
ans =
0.00000
0.69315
1.09861
>> exp(v)
ans =
2.7183
7.3891
20.0855
>> abs([-1;-2;-3])
ans =
1
2
3
>> -v % -1*v
ans =
-1
-2
-3
>> v+ones(length(v),1)
ans =
2
3
4
>> A' % ' meas transpose
ans =
1 3 5
2 4 6
>> (A')'
ans =
1 2
3 4
5 6
>> value=max(v)
value = 3
>> [value,index]=max(v)
value = 3
index = 3
>> v<2
ans =
1
0
0
>> [row,col]=find(A>=7)
row =
1
3
2
col =
1
2
3
>> a=[1.000 15.000 2.000 0.500]
a =
1.00000 15.00000 2.00000 0.50000
>> sum(a)
ans = 18.500
>> prod(a) % multiply
ans = 15
>> floor(a)
ans =
1 15 2 0
>> ceil(a)
ans =
1 15 2 1
>> max(rand(3),rand(3)) % For two matrices (or a matrix and a scalar), return the pairwise maximum.
ans =
0.86233 0.98616 0.82504
0.82724 0.70070 0.31207
0.89491 0.58022 0.97937
>> max(A,[],1)
ans =
8 9 7
>> max(A,[],2)
ans =
8
7
9
>> max(A)
ans =
8 9 7
>> max(max(A))
ans = 9
>> max(A(:))
ans = 9
>> A=magic(9)
A =
47 58 69 80 1 12 23 34 45
57 68 79 9 11 22 33 44 46
67 78 8 10 21 32 43 54 56
77 7 18 20 31 42 53 55 66
6 17 19 30 41 52 63 65 76
16 27 29 40 51 62 64 75 5
26 28 39 50 61 72 74 4 15
36 38 49 60 71 73 3 14 25
37 48 59 70 81 2 13 24 35
>> sum(A,1)
ans =
369 369 369 369 369 369 369 369 369
>> sum(A,2)
ans =
369
369
369
369
369
369
369
369
369
>> A .* eye(9)
ans =
47 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 68 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 8 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 20 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 41 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 62 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 74 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 14 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 35
>> sum(sum(A .* eye(9)))
ans = 369
>> flipud(eye(9))
ans =
Permutation Matrix
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
>> A=magic(3)
A =
8 1 6
3 5 7
4 9 2
>> pinv(A) % pseudoinverse of X 广义逆矩阵(伪逆矩阵)
ans =
0.147222 -0.144444 0.063889
-0.061111 0.022222 0.105556
-0.019444 0.188889 -0.102778
>> pinv(A) * A
ans =
1.0000e+00 2.0817e-16 -3.1641e-15
-6.1062e-15 1.0000e+00 6.2450e-15
3.0531e-15 4.1633e-17 1.0000e+00
part4: plot data
>> t=[0:0.01:0.98];
>> y1=sin(2*pi*4*t);
>> plot(t,y1);
>> y2=cos(2*pi*4*t);
>> plot(t,y2)
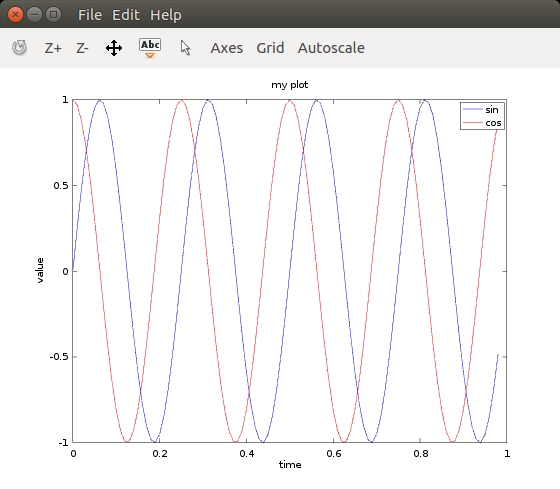
>> plot(t,y1);
>> hold on;
>> plot(t,y2,'r');
>> xlabel('time')
>> ylabel('value')
>> legend('sin','cos')
>> title('my plot')
>>
>> print -dpng 'myplot.png'
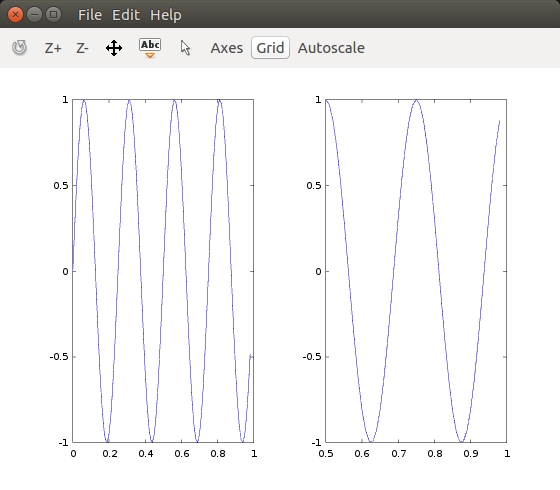
>> figure(1); plot(t,y1);
>> figure(2); plot(t,y2); % two figure windows
>> subplot(1,2,1) % divides plota 1x2 grid, access first element
>> plot(t,y1);
>> subplot(1,2,2);
>> plot(t,y2);
>> axis([0.5 1 -1 1])
>> clf; % clean plot
>> A=magic(5)
A =
17 24 1 8 15
23 5 7 14 16
4 6 13 20 22
10 12 19 21 3
11 18 25 2 9
>> imagesc(A)
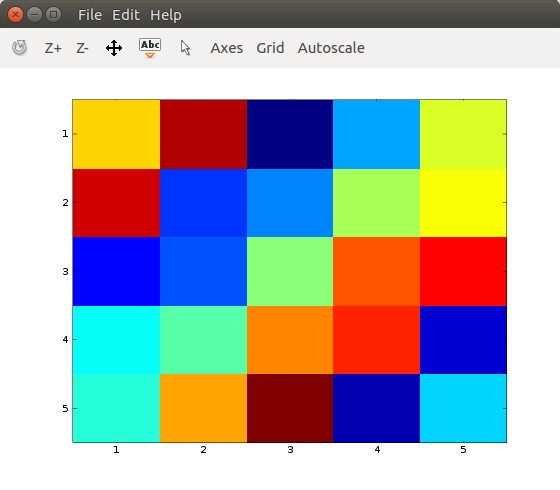
>> imagesc(A)
>> imagesc(A), colorbar, colormap gray;
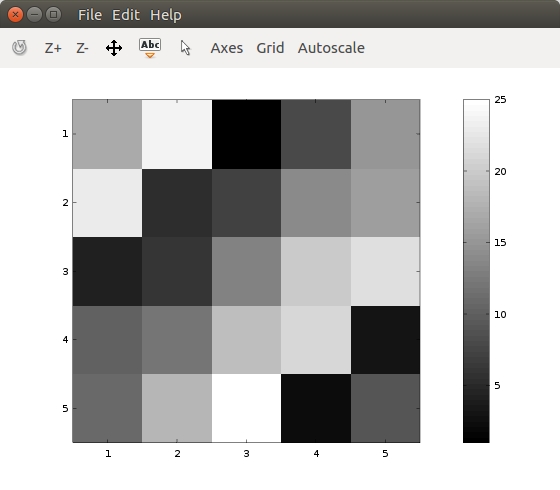
part5: control statement
>> v=zeros(10,1);
>> for i=1:10,
v(i)=2^i;
end;
>> v
v =
2
4
8
16
32
64
128
256
512
1024
>> indices=1:10;
>> for i=indices,
disp(i);
end;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
>> i=1;
>> while i<=5,
v(i)=100;
i=i+1;
end;
>> v
v =
100
100
100
100
100
64
128
256
512
1024
>> i=1;
>> while true,
v(i)=999;
i=i+1;
if i==6,
break;
end;
end;
>> v
v =
999
999
999
999
999
64
128
256
512
1024
>> v(1)=2;
>> if v(1)==2,
disp('v(1) is two');
elseif v(1)==1,
disp('v(1) is one');
else
disp('v(1) is not one or two');
end;
v(1) is two
function
%squareThisNumber.m
function y = squareThisNumber(x)
y = x^2;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
>> squareThisNumber(5)
ans = 25
>> squareThisNumber(5)
ans = 25
>> % Octave search path
>> addpath('someplace')
%squareAndCubeThisNumber.m
function [y1,y2] = squareAndCubeThisNumber(x)
y1 = x^2
y2 = x^3
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
>> [a,b]=squareAndCubeThisNumber(2)
y1 = 4
y2 = 8
a = 4
b = 8
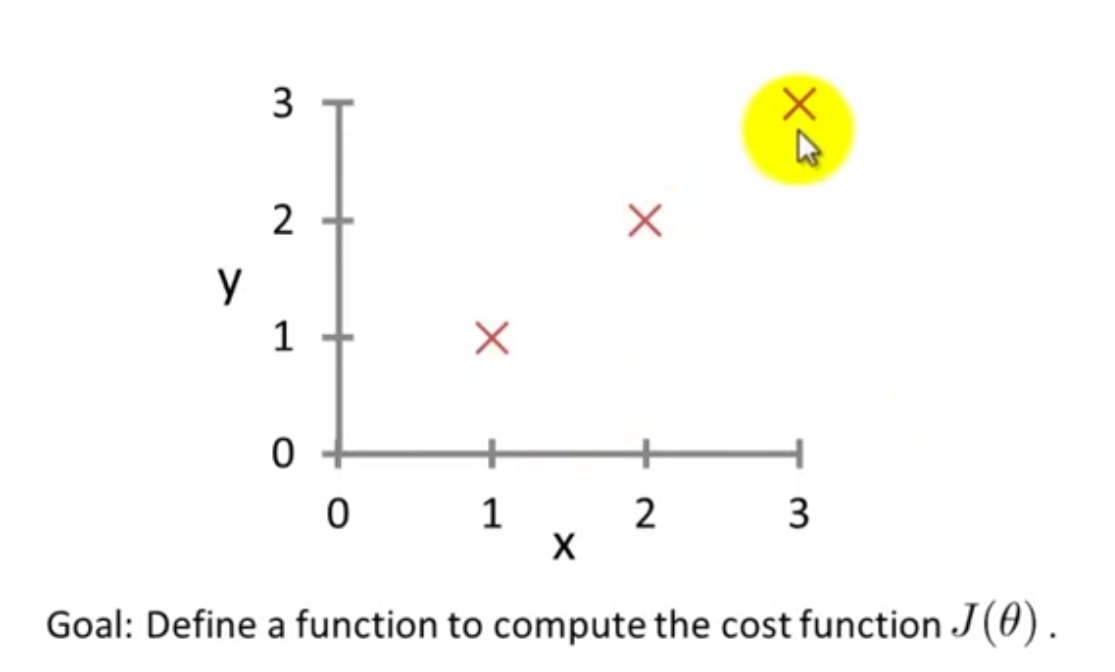
%costFunctionJ.m
function J = costFunctionJ(X, y, theta)
% X is the "design matrix" containing our training examples
% y is the class labels
m = size(X, 1); % number of training examples
predictions = X*theta; % predictions of hypothesis on all m examples
sqrErrors = (predictions - y).^2; % squared errors
J = 1/(2*m) * sum(sqrErrors);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
>> X=[1 1;1 2;1 3];
>> y=[1;2;3];
>> theta=[0;1];
>> j=costFunctionJ(X,y,theta)
j = 0
>> theta=[0;0];
>> j=costFunctionJ(X,y,theta)
j = 2.3333
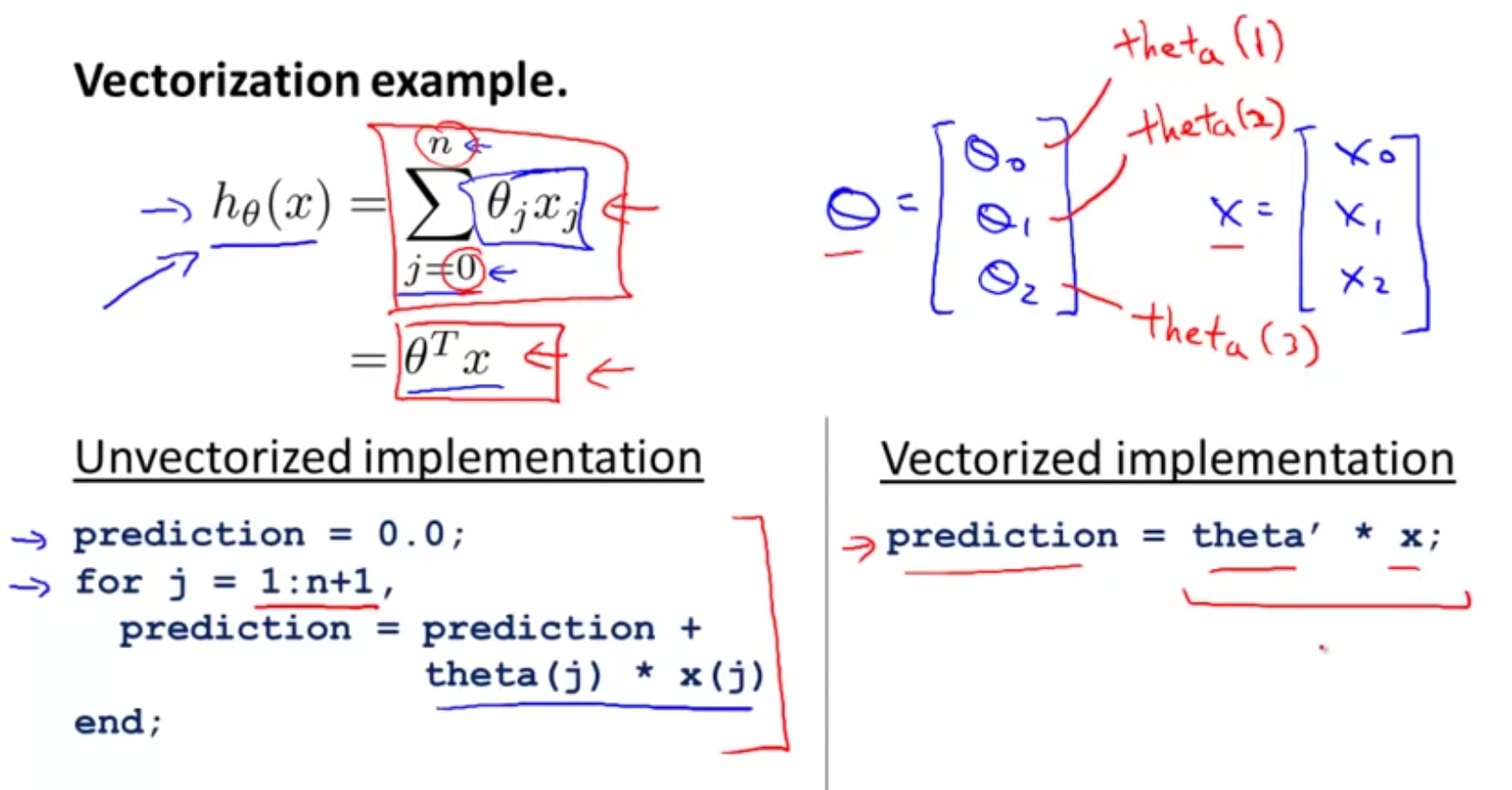
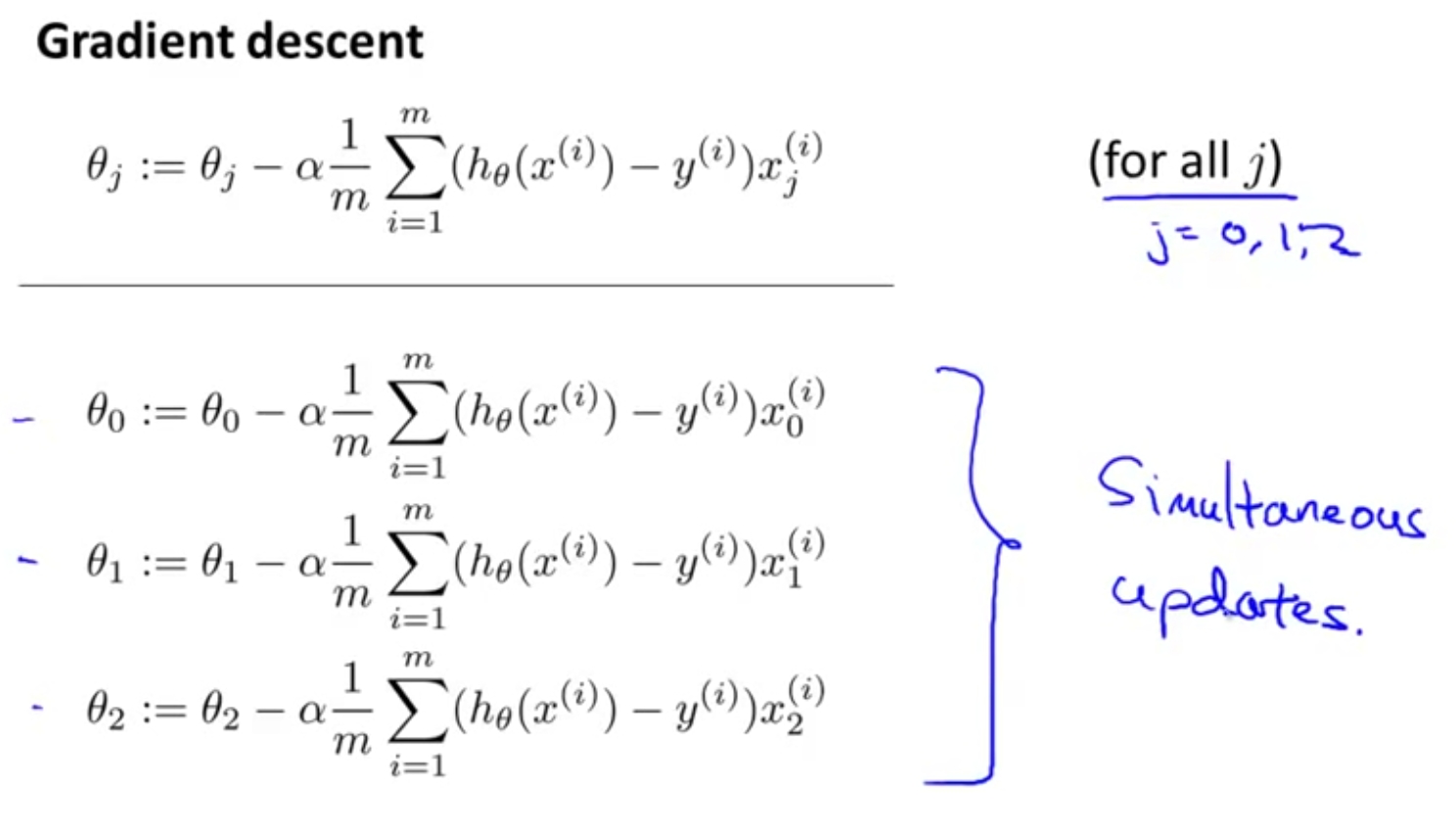
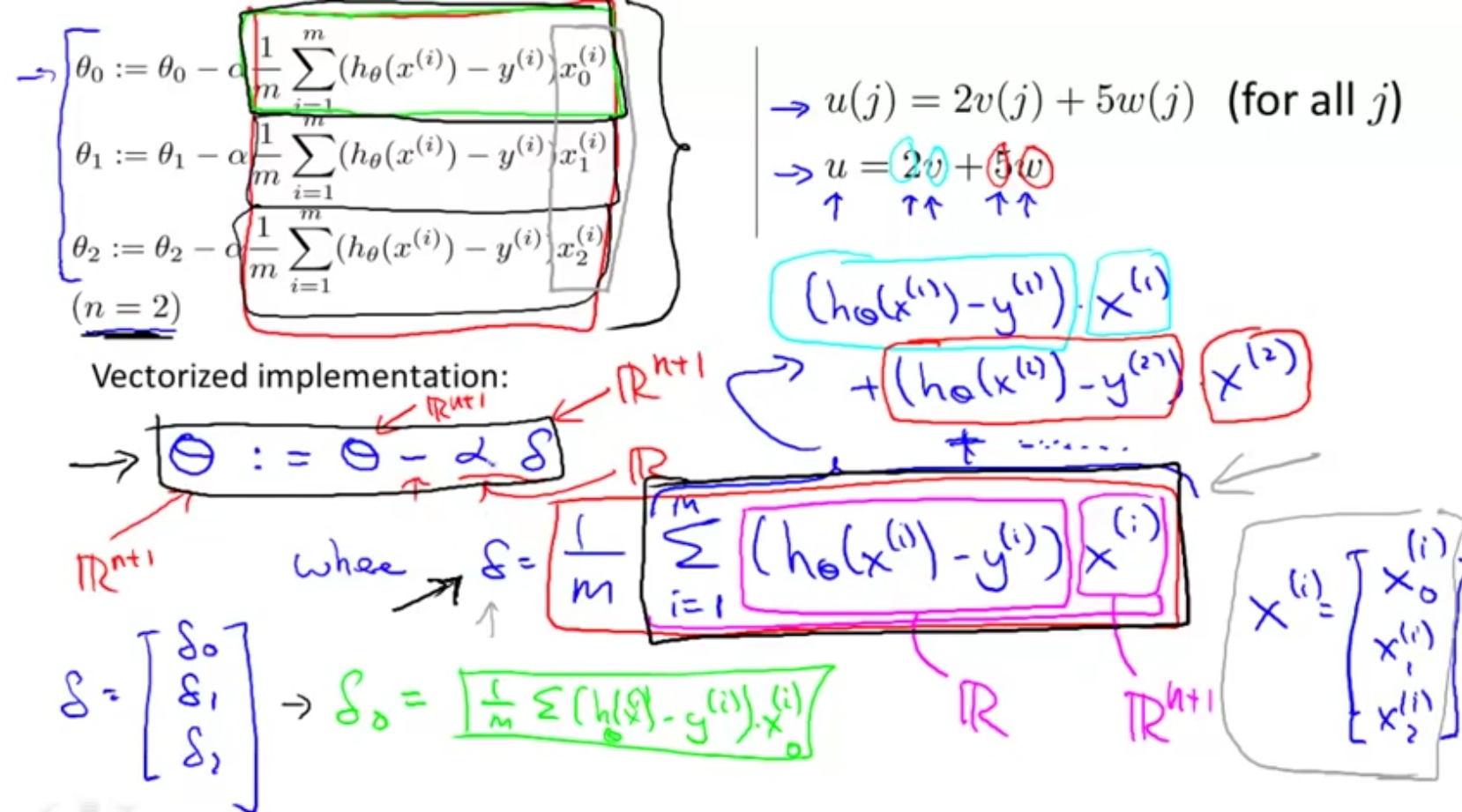
part6: Vectorization