how MVC works in TD
Updated at: February 27, 2017
shared by Prakash Wilbert @eBay
Here is how it Works?
The compress algorithm examines the characteristics of variables and looks for eliminating repeated patterns and compresses the unused space.
For example: Let’s say a flag is defined as BYTEINT data type which stores values 0 or 1, by default BYTEINT occupies 8 bits. The value 0 or 1 stores only 1 bit and remaining 7 bits will be wasted. Think of for 1Mn rows of records there are 7Mn bits are wasted.
Using compress statement we can compresses all unused bits on the relevant flag and saves the wasted unused bits across rows.
| Without compress technique | With compress technique |
|---|---|
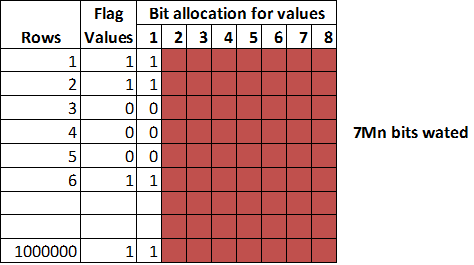 |
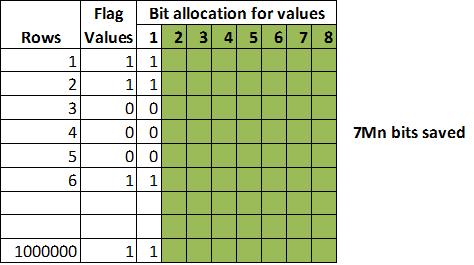 |
How does one use it?
For example table dummy which contains 3 attributes (cust_id, counter_prty and available_balance), out of these 3 variables the best variable to use compress is “available_balance” which contains frequent values of 0 or 1 available in the source.
Step1: Create empty table with structure.
create table dummy
( CUST_ID CHAR(20) CHARACTER SET LATIN NOT CASESPECIFIC,
COUNTER_PRTY CHAR(20) CHARACTER SET LATIN NOT CASESPECIFIC,
AVAILABLE_BALANCE BYTEINT COMPRESS (0 ,1 ) – Define compress statement by assigning frequent value used in that attribute.
) primary index (cust_id, PRTY);
Step2: insert the data into created empty structured table
Insert into dummy
sel * from source_table
Space savings in action:
We leveraged this technique for attempt level GDD data and have realized > 50% of space savings. On average each month is ~ 90GB in size which dropped to ~ 40GB after using Compress.